برای اینکه نصب مدیر بوت در لینوکس را انجام دهیم اول باید یک توضیح درباره چطور اجرا شدن سیستم عامل بدهیم. زمانی که سیستم را روشن می کنیم اول BIOS که یک حافظه فقط خواندنی هستش یکسری از موارد را چک می کند و سپس عملیات POST اتفاق می افتد، عملا POST یکسری تست است که سخت افزار را برسی میکند مانند اروری که گاهی باید F1 بزنیم.
حالا بعد از این که POST با موفقیت کارش تمام شود MBR یا master boot record که قبلا در پست قبل”طراحی لی آوت هارد دیسک (Design hard disk layout)) درباره آن صحبت کردیم عملیات را بدست می گیرد. همانطور که قبلا گفتیم MBR فقط 512 بایت اول هارد است.
حالا برای این که بتوانید سیستم عامل را لود کنید و یا چند سیستم عامل در کنار هم نصب کنید نیاز به یک smart bootloader داریم که در نسخه های قدیمی لینوکس به آن LILO گفته می شد ولی امروزه از GRUB و GRUB2 استفاده می شود.
زمانی که یک بوت لودر عملیات را به بوت لودر دیگری انتقال می دهد به آن Chain Loading گفته می شود مانند زمانی که GRUB می خواهد عملیات بوت رو به دست سیستم عامل ویندوز بدهد.
LILO چیست؟
LILO مخفف کلمات Linux Loader است و همانطور که از نامش هم پیداست Boot Loader ای است که ویژه سیستم عامل لینوکس طراحی و پیاده سازی شده است. LILO در واقع کدی است که BIOS در هنگام Startup سیستم در داخل حافظه کامپیوتر Load می کند. همانند GRUB بوت لودر LILO هم می تواند سیستم عامل ها را از یک منبع خارجی مثل فلاپی دیسک یا هارد دیسک اکسترنال boot کند.
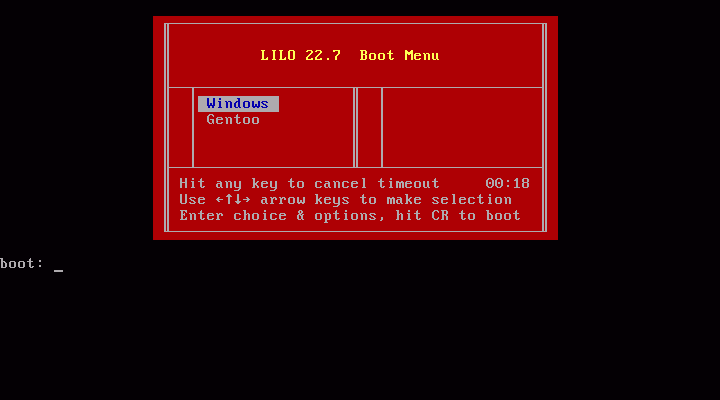
کاری که LILO در چنین حالتی انجام می دهد این است که Master Boot Record یا MBR را روی دستگاه خارجی نصب می کند و با این حالت براحتی در زمان بوت سیستم Kernel سیستم عامل را پیدا می کند و آن را داخل حافظه RAM سیستم Load می کند و سیستم عامل را بالا می آورد.
تنظیمات آن در مسیر زیر قرار دارد:
/etc/lilo.conf
و با استفاده از دستور زیر هم LILO نصب و کانفیگ می شود:
/usr/sbin/liloconfig
که محتوای فایل بالا به صورت زیر می باشد:
# Originally generated by liloconfig - modified by Ian Shields
# This allows booting from any partition on disks with more than 1024
# cylinders.
lba32
# Specifies the boot device (floppy) از کجا بوت انجام شود
boot=/dev/fd0
# Specifies the device that should be mounted as root.
# If the special name CURRENT is used, the root device is set to the
# device on which the root file system is currently mounted. If the root
# has been changed with -r , the respective device is used. If the
# variable ROOT is omitted, the root device setting contained in the
# kernel image is used. It can be changed with the rdev program.
root=/dev/sda7
# Bitmap configuration for /boot/coffee.bmp
# رنگ بندی را مشخص کرده است
bitmap=/boot/coffee.bmp
bmp-colors=12,,11,15,,8
bmp-table=385p,100p,1,10
bmp-timer=38,2,13,1
# Enables map compaction:
# Tries to merge read requests for adjacent sectors into a single
# read request. This drastically reduces load time and keeps the map
# smaller. Using COMPACT is especially recommended when booting from a
# floppy disk.
compact
# Install the specified file as the new boot sector.
# LILO supports built in boot sectors, you only need
# to specify the type, choose one from 'text', 'menu' or 'bitmap'.
# new: install=bmp old: install=/boot/boot-bmp.b
# new: install=text old: install=/boot/boot-text.b
# new: install=menu old: install=/boot/boot-menu.b or boot.b
# default: 'menu' is default, unless you have a bitmap= line
# Note: install=bmp must be used to see the bitmap menu.
# install=menu
install=bmp
# Specifies the number of _tenths_ of a second LILO should
# wait before booting the first image. LILO
# doesn't wait if DELAY is omitted or if DELAY is set to zero.
# delay=20
# Prompt to use certain image. If prompt is specified without timeout,
# boot will not take place unless you hit RETURN. Timeout is in tenths of
# a second.
prompt
timeout=200
# Enable large memory mode.
large-memory
# Specifies the location of the map file. If MAP is
# omitted, a file /boot/map is used.
map=/boot/map
# Specifies the VGA text mode that should be selected when
# booting. The following values are recognized (case is ignored):
# NORMAL select normal 80x25 text mode.
# EXTENDED select 80x50 text mode. The word EXTENDED can be
# abbreviated to EXT.
# ASK stop and ask for user input (at boot time).
# <number> use the corresponding text mode. A list of available modes
# can be obtained by booting with vga=ask and pressing [Enter].
vga=normal
# Defines non-standard parameters for the specified disk.
#disk=/dev/sda
# bios=0x80
# If you are using removable USB drivers (with mass-storage)
# you will need to tell LILO to not use these devices even
# if defined in /etc/fstab and referenced in /proc/partitions.
# Adjust these lines to your devices:
#
# disk=/dev/sda inaccessible
# disk=/dev/sdb inaccessible
# These images were automagically added. You may need to edit something.
# ایمیج ها و مسیر های سیستم عامل های مختلف را مشخص کرده است
# که در این جا سه سیستم عامل قرار گرفته است
image=/boot/vmlinuz-2.6.31-14-generic
label="Lin 2.6.31-14"
initrd=/boot/initrd.img-2.6.31-14-generic
read-only
image=/boot/vmlinuz-2.6.31-20-generic
label="Lin 2.6.31-20"
initrd=/boot/initrd.img-2.6.31-20-generic
read-only
image=/boot/memtest86+.bin
label="Memory Test+"
read-only
# If you have another OS on this machine (say DOS),
# you can boot if by uncommenting the following lines
# (Of course, change /dev/sda1 to wherever your DOS partition is.)
other=/dev/sda6
label="Fedora 8"
other=/dev/sda1
label="Windows XP"تا اینجای کار ما فقط فایل تنظیمات را ساختیم و ویرایش کرده ایم ولی برای نصب LILO باید دستور زیر را وارد کنیم:
lilo -v -vنکته: -v به معنی verbosity است و در این دستور چون خواستیم توضیحات بیشتری به ما نمایش دهد دوبار -v استفاده کرده ایم.
خروجی دستور بالا و تنظیماتی که در فایل کانفیگ وارد کردیم به صورت زیر است:
# lilo -v -v
LILO version 22.8, Copyright (C) 1992-1998 Werner Almesberger
Development beyond version 21 Copyright (C) 1999-2006 John Coffman
Released 19-Feb-2007, and compiled at 10:52:38 on Aug 25 2009
Running Linux kernel 2.6.31-14-generic on i686
Ubuntu
raid_setup returns offset = 00000000 ndisk = 0
BIOS VolumeID Device
Reading boot sector from /dev/fd0 طبق تنظیمات گفته بودیم روی فلاپی نصب شود
pf_hard_disk_scan: ndevs=1
0800 54085408 /dev/sda
device codes (user assigned pf) = 0
device codes (user assigned) = 0
device codes (BIOS assigned) = 1
device codes (canonical) = 1
mode = 0x03, columns = 80, rows = 25, page = 0
Using BITMAP secondary loader
Calling map_insert_data
Secondary loader: 19 sectors (0x3800 dataend).
Warning: The boot sector and map file are on different disks.
bios_boot = 0x00 bios_map = 0x80 map==boot = 0 map S/N: 54085408
Mapping bitmap file /boot/coffee.bmp
Calling map_insert_file
Compaction removed 592 BIOS calls.
Bitmap: 603 sectors.
BIOS data check was okay on the last boot
Boot image: /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.31-14-generic
Setup length is 26 sectors.
Compaction removed 7452 BIOS calls.
Mapped 7601 sectors.
Mapping RAM disk /boot/initrd.img-2.6.31-14-generic
Compaction removed 14696 BIOS calls.
RAM disk: 14930 sectors.
Added Lin_2.6.31-14 *
Boot image: /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.31-20-generic
Setup length is 26 sectors.
Compaction removed 7468 BIOS calls.
Mapped 7617 sectors.
Mapping RAM disk /boot/initrd.img-2.6.31-20-generic
Compaction removed 14704 BIOS calls.
RAM disk: 14938 sectors.
Added Lin_2.6.31-20
Boot image: /boot/memtest86+.bin
Setup length is 4 sectors.
Compaction removed 243 BIOS calls.
Mapped 254 sectors.
Added Memory_Test+
Boot other: /dev/sda6, loader CHAIN
Pseudo partition start: 43198848
Compaction removed 0 BIOS calls.
Mapped 6 (4+1+1) sectors.
Added Fedora_8
Boot other: /dev/sda1, on /dev/sda, loader CHAIN
Compaction removed 0 BIOS calls.
Mapped 6 (4+1+1) sectors.
Added Windows_XP
BIOS VolumeID Device
80 54085408 0800
Writing boot sector.
/boot/boot.0200 exists - no boot sector backup copy made.
Map file size: 336896 bytes.
RAID device mask 0x0000
One warning was issued.برخی از سوئیچ های دستور LILO:
| switch | meaning |
|---|---|
| -q | show information about the map file. map file is located at /boot/map and contains the boot configs |
| -R | boot the system on the next reboot only. Used for remote systems |
| -l | list information about the Kernel |
| -u | uninstall lilo and restore previous boot record |
Grub چیست و بررسی بارگذاری راه انداز Grub
GRUBv1 یا دقیقتر ورژن 0.9 است که به آن GRUB Legacy هم می گویند که عملا دیگه هیچ جایی استفاده نمی شود. GRUB هم یک Boot Loder هست و کارش دقیقا مثل LiLo و دیگر Boot Loder است البته با ویژگی های خاص خودش.
/boot/grub/menu.lst : حاوی اطلاعات مربوط به پارتیشن ها یا سیستم عامل هایی است که سیستم می تواند به وسیله آنها راه اندازی شود.
/etc/grub.conf : این فایل حاوی پارامترهایی است که پوسته GRUB جهت نصب صحیح بارگذار به انها نیاز دارد.
/boot/grub/device.map : فایل مذکور نام قطعاتی که در GRUB و BIOS ذکر شده اند را به نام های معادلشان در لینوکس تبدیل می کند و در واقع مترجمی بین سیستم عامل و BIOS است که توسط آن دیگر فایل های پیکربندی، پارتیشن های سیستم را تشخیص می دهند.
محتوایات فایل grub.conf در ورژن یک GRUB به صورت دیفالت زیر می باشد:
# grub.conf generated by anaconda
#
# Note that you do not have to rerun grub after making changes to this file
# NOTICE: You do not have a /boot partition. This means that
# all kernel and initrd paths are relative to /, eg.
# root (hd0,5)
# kernel /boot/vmlinuz-version ro root=/dev/sda6
# initrd /boot/initrd-version.img
#boot=/dev/sda6
default=1
#یعنی اولی بوت شود
timeout=10
#یعنی اگر 10 ثانیه کاری نکردم اجرا کن
splashimage=(hd0,5)/boot/grub/splash.xpm.gz
#hiddenmenu
password --md5 $1$RW1VW/$4XGAklxB7/GJk0uO47Srx1
#زمان بوت یک پسورد می خواهد که اینجا به صورت هش شده نوشته شده است
#باقی موارد هم عنوان های من است
title Upgrade to Fedora 11 (Leonidas)
kernel /boot/upgrade/vmlinuz preupgrade \
repo=hd::/var/cache/yum/preupgrade stage2=\
hd:UUID=8b4c62e7-2022-4288-8995-5eda92cd149b:/boot/upgrade/install.img \
ks=hd:UUID=8b4c62e7-2022-4288-8995-5eda92cd149b:/boot/upgrade/ks.cfg
initrd /boot/upgrade/initrd.img
title Fedora (2.6.26.8-57.fc8)
root (hd0,5)
kernel /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.26.8-57.fc8 ro root=LABEL=FEDORA8 rhgb quiet
initrd /boot/initrd-2.6.26.8-57.fc8.img
title Fedora (2.6.26.6-49.fc8)
root (hd0,5)
kernel /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.26.6-49.fc8 ro root=LABEL=FEDORA8 rhgb quiet
initrd /boot/initrd-2.6.26.6-49.fc8.img
title GRUB Menu
rootnoverify (hd0,1)
chainloader +1
title Windows
rootnoverify (hd0,0)
chainloader +1در زیر بخشی از آپشن های فایل بالا را اورده ایم:
| command | meaning |
|---|---|
| # | comment |
| default | the default system to boot; starts from 0 |
| timeout | how long to wait before autobooting |
| splashimage | background image |
| password | Security is important! will ask this password |
| title | Name of the entery |
| root | The partion to boot. Counting starts from 0. root(hd0,2) is the 3rd partion on the first disk |
| kernel | which kernel image should be loaded |
| initrd | the name of the initial RAM disk. Modules needed by the kernel before the file system is mounted |
| savedefault | remember the last booted item |
| chainloader | another file will act as stage 1 loader. Used for booting Windows systems |
نصب GRUB legacy
بعد از این که تنظیمات گراب را انجام دادیم باید با استفاده از روت و دستور زیر آن را نصب کنیم:
# grub-install /dev/fd0
یا
# grub-install '(fd0)'GRUB2 چیست؟
درحال حاضر بیشترین استفاده در لینوکس های امروزی GRUBv2 می باشد که فایل تنظیمات آن در /boot/grub/grub.cfg قرار دارد که محتویات آن چیزی شبیه به زیر است:
### BEGIN /etc/grub.d/05_debian_theme ###
set menu_color_normal=white/black
set menu_color_highlight=black/white
### END /etc/grub.d/05_debian_theme ###
### BEGIN /etc/grub.d/10_linux ###
menuentry "Ubuntu, Linux 2.6.31-20-generic" {
recordfail=1
if [ -n ${have_grubenv} ]; then save_env recordfail; fi
set quiet=1
insmod ext2
set root=(hd0,7)
search --no-floppy --fs-uuid --set 8954fa66-e11f-42dc-91f0-b4aa480fa103
linux /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.31-20-generic \
root=UUID=8954fa66-e11f-42dc-91f0-b4aa480fa103 ro quiet splash
initrd /boot/initrd.img-2.6.31-20-generic
}
menuentry "Ubuntu, Linux 2.6.31-20-generic (recovery mode)" {
recordfail=1
if [ -n ${have_grubenv} ]; then save_env recordfail; fi
insmod ext2
set root=(hd0,7)
search --no-floppy --fs-uuid --set 8954fa66-e11f-42dc-91f0-b4aa480fa103
linux /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.31-20-generic
root=UUID=8954fa66-e11f-42dc-91f0-b4aa480fa103 ro single
initrd /boot/initrd.img-2.6.31-20-generic
}حال بعد تغییرات فایل کانفیگ می توان با دستور grub-install /dev/sda آن را در /dev/sda و بر روی MBR نصب کرد.
فایل راهنمای (Help) گراب هم به صورت زیر است که در ساخت آن می تواند به شما کمک کند:
$ grub-install --help
Usage: grub-install [OPTION] install_device
Install GRUB on your drive.
-h, --help print this message and exit
-v, --version print the version information and exit
--modules=MODULES pre-load specified modules MODULES
--root-directory=DIR install GRUB images under the directory DIR
instead of the root directory
--grub-setup=FILE use FILE as grub-setup
--grub-mkimage=FILE use FILE as grub-mkimage
--grub-mkdevicemap=FILE use FILE as grub-mkdevicemap
--grub-probe=FILE use FILE as grub-probe
--no-floppy do not probe any floppy drive
--recheck probe a device map even if it already exists
--force install even if problems are detected
--disk-module=MODULE disk module to use
INSTALL_DEVICE can be a GRUB device name or a system device filename.
grub-install copies GRUB images into the DIR/boot directory specified by
--root-directory, and uses grub-setup to install grub into the boot
sector.
Report bugs to <bug-grub@gnu.org>.همچنین اگر تنظیماتی از قبل وجود ندارد می توان با دستور grub-mkconfig یک تنظیمات پیشفرض ایجاد کرد.